Different makeup products are used to enhance different body parts likewise we have different types of accounts categorizing the transactions under different heads. Each of these accounts forms the pillars of the Accounting transactions. Golden rules of Accounting or Bookkeeping rules lays the foundation of Journal Entries. Remembering the Golden Rules of Accounting is important to frame correct journal entries to be recorded in the books of accounts. These books serve as historical data reservoirs.
There are mainly three types of accounts in accounting: Real, Personal, and Nominal Accounts. There are 3 Golden Rules of Accounting associated with each of these 3 accounts. Let us study all these three Golden rules of Accounting with examples and know the tricks to remember them throughout.
Table of Contents
Golden Rules of Accounting
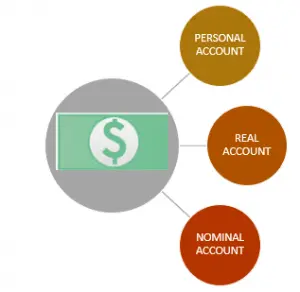
- Personal Account- Debit the Receiver, Credit the Giver.
Example- Assume you have sold an asset to your friend, you become the Giver here. Since you sold an asset and received cash in return, therefore you are Credited. Your friend who received the asset becomes the Receiver. Since he paid cash to you, he is Debited. This is the 1st among the Golden Rules of Accounting.
Friend A/c – Dr.
To Your A/c
Easy remembrance– Personal account as the name suggests is related to a person. To remember the journal entry related to personal account use “Dog races, Cat gazes .” “Receiver is debited, Giver is credited.” Where Dog represents Debit, and Cat as credit. Or another way to remember is DRCG, taking the 1st letters of the four words.
- Real Account– Debit What Comes In, Credit What Goes Out.
Example- Reversing the above example, suppose you buy an asset that may be mobile from your friend. Mobile that you receive in the form of the asset makes Asset Account Debited. You give cash for that, so Credit the Cash Account. In case we reverse the example where you sell an asset to your friend. The asset is received by your friend whereas cash is received by you. A cash account is Debited & Asset Account is Credited. This is 2nd among Golden Rules of Accounting.
Asset A/C – Dr
To Cash A/C
Easy remembrance– Real account as the name suggests refers to something real & tangible. To remember the journal entry related to Real Account use “Dog wags tail when someone comes in, Cat screams when someone goes out.” Where Dog represents Debit, and Cat as credit.
- Nominal Account– Debit All Expenses and Losses, Credit All Incomes and Gains.
Example- You are selling an asset to your friend at profit. A cash account is Debited, and Profit gets Credited as Credit for all the Income & Gains. This is the last of the Golden Rules of Accounting.
Cash A/C – Dr
To Profit on Sale of Asset
Easy remembrance– Nominal account as the name suggests refers to a measure of value. To remember the journal entry related to nominal account use.” Dogs carry expenses, which may lead to losses, whereas cats save income and lead to gains. Where Dog represents Debit, and Cat as credit.
In accounting the above 3 journal entries related to Personal, Real, and Nominal accounts popularly known as the Golden Rules of Accounting are also known as the “Thumb Rule of Accounting”. It is because all the journal entries are based on the above 3 principles. You need to identify each entry based on the above 3 accounts, and then frame the respective journal entries. Once you byheart the Golden Rules of Accounting, then the formation of journal entries will become the easiest task ever.

Why were these Golden Rules of Accounting framed?
The process of recording expenses and income goes back in history. Earlier the transactions were recorded, but determining the surplus of deficit amount was not easy. Besides, there was no way to identify any errors committed while recording individual economic transactions. There had always been a need for a standard system that helps in recording the economic transactions in a way that it could help anyone to analyze the financial status, know the dues, understand their liabilities, also check the profits realized within no time. Thus Golden Rules of Accounting were framed to ensure that transactions were recorded correctly using the double-entry system. Golden Rules of Accounting helped in the below ways:
- Categorizing the economic transactions
- Having standardized Rules of treating a transaction
- Uniformity across
- Maintain Historic data for future reference
- Easy review and analysis
- Auditing becomes easy
Accounting and Golden Rules of Accounting
Accounting is the process of identifying, measuring, and communicating economic information to permit informed judgments and decisions by the use of the information. According to the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA): “Accounting is an art of recording, classifying and summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money, transactions, and events which are, in part at least, of a financial character, and interpreting the results thereof.”
- Accounting is the systematic recorded presentation of the financial activities of the business
- It is the systematic record-keeping of all that happens in a business on a day-to-day basis. (Chronological basis).
- In simple words ‘Accounting’ merely means: ‘reckoning’ or ‘recounting’
- Accounting may be defined as the process of collecting, recording, summarising & communicating financial information
Golden Rules of Accounting are used in the 1st step of the Accounting Process. It forms the base, and if the base is strong the rest will follow in order. Thus becomes important to byheart the Golden Rules of Accounting while practicing to frame journal entries for various types of economic transactions.
Accounting Process:
The Accounting Process consists of the following four Stages:
- Recording the Transaction
- Classifying the Transaction
- Summarizing the Transaction
- Interpreting the results
- Recording the Transactions: The accounting process begins with a recording of all transactions in the book of original entry. This book is called ‘Journal’. All transactions are recorded in the Journal in chronological order (date wise) with the help of various vouchers or receipts such as cash memos, cash receipts, invoices, etc. Any transaction recorded follows the double-entry system based on the Golden Rules of Accounting.
- Classifying the Transactions: The second stage consists of grouping the transactions of similar nature and posting them to the concerned accounts in another book called ‘Ledger’. For example, all transactions related to cash are posted to Cash Account and the transactions related to different persons are entered separately in the account of each person. The objective of classifying the transactions in this manner is to ascertain the combined effect of all transactions of a given period in respect of each account. For this purpose, all accounts are balanced periodically.
- Summarizing the Transactions: The next step is to prepare a year-end summary known as ‘Final Accounts’. But before preparing the final accounts, we prepare a statement called Trial Balance in order to check the arithmetical accuracy of the book of account. If the Trial Balance tallies, it means that the transactions have been currently recorded and posted into the ledger. Then, with the help of the Trial Balance and some other relevant information we prepare the final accounts. The objectives of preparing the final accounts are (I) to know the net result of business activities and (ii) to ascertain the financial position of the business. The final account consists of an income statement called ‘Trading and Profit and Loss Account gives us the information about the amount of profit made or the loss incurred during the year and the Balance Sheet shows the position of assets and liabilities of the business as at the end of the year.
- Interpreting the Results: The last stage consists of analyzing and interpreting the results shown by the final accounts. This involves the computation of various accounting ratios to assess the liquidity, solvency, and profitability of the business. Such analysis is meant for interested parties like management, investors, bankers, creditors, etc. The balances on various accounts appearing in the Balance Sheet will then be transferred to the new books of account for the next year. Thereafter the process of recording transactions for the next year starts again.
Funfact:
- Did you know that the Golden Rules of Accounting, Accounting Concepts, and Double Entry System was invented by Luca Pacioli, known as the Father of Accounting?
Let us know if our easy remembering tricks to memorize Golden Rules of Accounting helped you?

Buy Highest Quality Dog Food


