Let’s understand the concepts of Financial Markets and Institutions in detail. The structure of Financial markets and Institutions can help you understand how it works, differences in structure, and lots more.
Table of Contents
Formal and Informal Financial System
As we all know the difference between a Parent’s Teacher Meeting and a Birthday party, same applies to the formal and informal financial system. Below is the difference between Formal & Informal Financial Systems.
| Formal Financial System | Informal Financial System |
| Organized sector | Unorganized sector |
| Regulated by Government and RBI | Unregulated |
| Consists of financial institutions and Banks | Consists of rural money lenders |
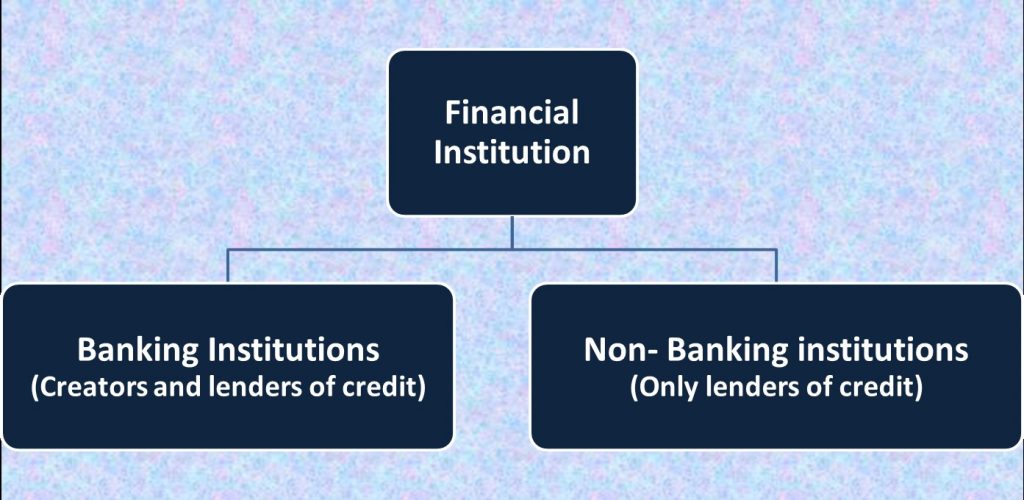
Financial Institutions
Just like schools /colleges act as the link between the education system and how it trickles down to us. Similarly, Financial institutions like Banks & Non – Banking institutions also act as links from where the financial system trickles down.
These are intermediaries that mobilize savings and facilitate the allocation of funds in an efficient manner.
These are claims against a person or an institution for payment, at a future date, of a sum of money and/ or a periodic payment in the form of interest or dividend.
Types of Financial Instruments
- Equity
- Debentures
- Bonds
- Money market instruments
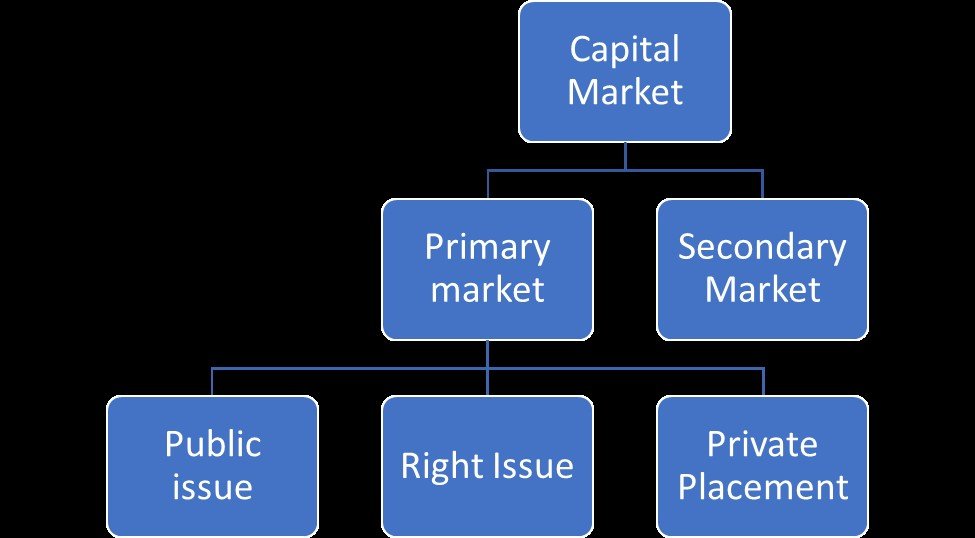
Capital Market & Money Market
The Capital Market is split into Primary & Secondary Market, & Primary Market is further split into Public issues, Rights Issues & Private Placement.
Difference Between Capital & Money Market
| Money Market | Capital Market |
| Short term market for financial assets with a maturity period of less than a year | Long term market for financial assets |
| Total volume per day is very high | Total volume per day is comparatively low |
| Participants are large institutional investors, commercial banks, mutual funds, etc | Even a small investor can deal by buying shares, debentures, or mutual funds |
Money Market
- It is a market for short term financial assets with maturity period of less than one year.
- It provides a mechanism to balance the demand for and supply of short-term funds.
- Is the opportunity for players to invest their short-term surplus funds and to borrow short-term funds in case of deficit.
Difference Between Primary Market & Secondary Market
| Primary market | Secondary Market |
| Deals with new securities | The market for existing securities, which are already listed |
| Provides additional capital to issuer companies | No additional capital was generated. Provides liquidity to existing stock |
All of the above collectively form Financial Markets and Institutions. The components form the structure of this system and aim at creating a balance of the financial economy.
Funfact
Indian’s Equity Capital market was $33.4 Billion in Sep 2020, which’s higher compared to the previous year.

